Mapping Software and GIS Glossary
Mapping tools are software programs or online applications that allow users to view, create, and interact with maps and other geographic data. These tools are essential for understanding the relationships between locations, distances, and other geographic information. Popular mapping tools include Maptitude Mapping Software, Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, MapBox, and Carto. Each of these tools offers features such as satellite imagery, terrain maps, search capabilities, and route-planning capabilities that make them invaluable for a wide range of applications.
Mapping tools in GIS are software programs or functionalities that allow for the creation, manipulation, and analysis of spatial data. These tools enable users to visualize and understand geographic patterns, relationships, and trends. Examples of mapping tools in GIS include geocoding, analysis tools, and geoprocessing.
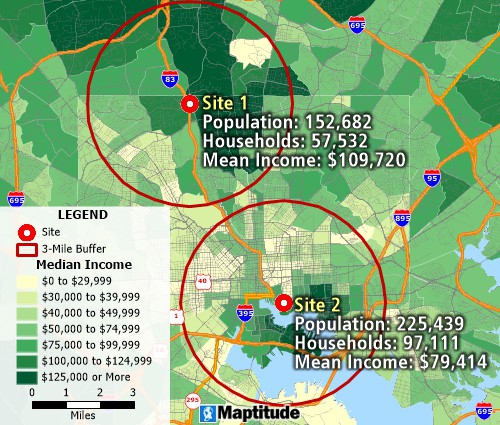
Overlay mapping tools can estimate and compare demographics in different locations
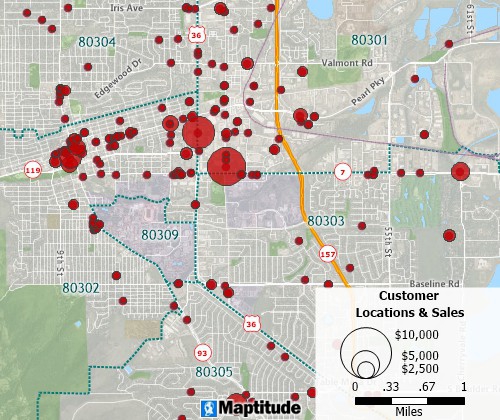
Geocoding tools can create pin maps by address, postal code, coordinate, and more
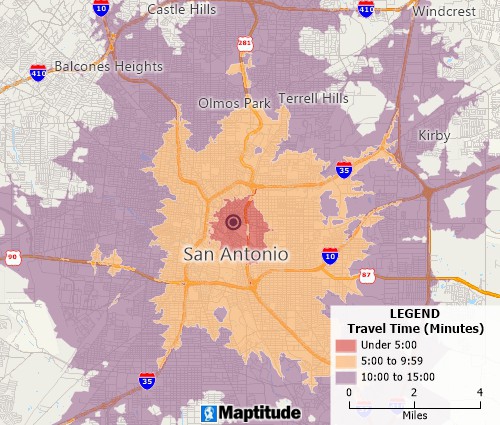
Drive-time ring mapping tools can determine accessibility at any interval
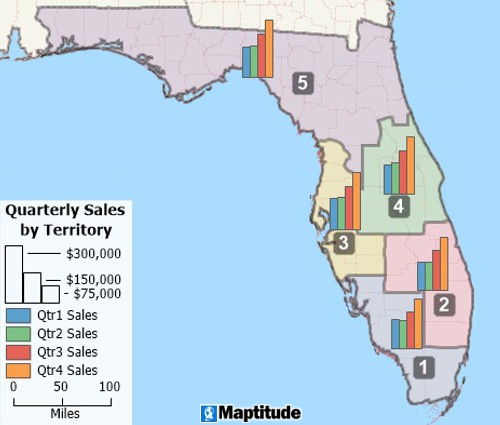
Territory mapping tools can create custom territories based on areas, proximity, or drive time
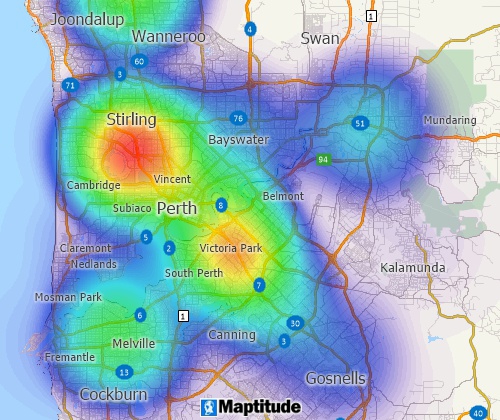
Heat map tools can identify weighted concentrations of features and over- and under-served areas
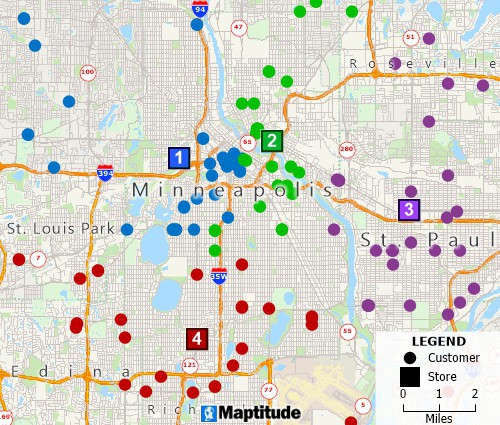
Mapping tools can filter features based on location and geographic attributes as well as conditional data attributes
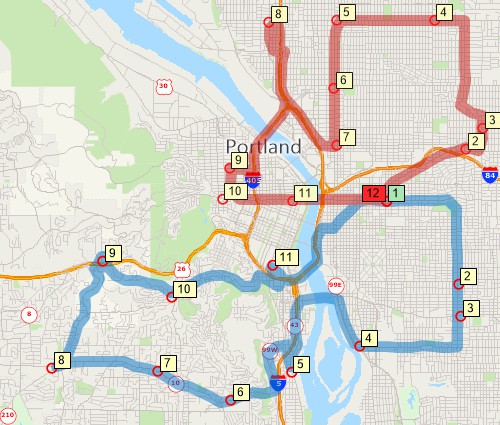
Routing and logistics mapping tools can find shortest and fastest routes
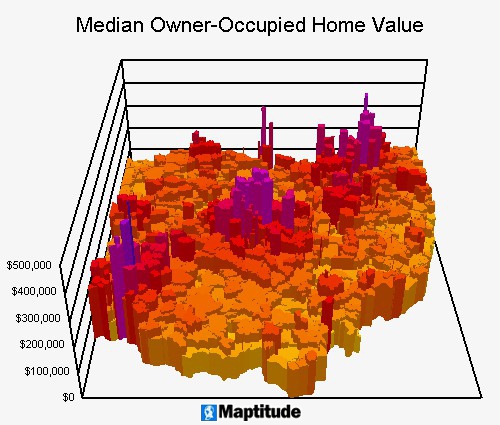
Mapping tools can illustrate geographic patterns with color, size, charts, 3D maps, and more
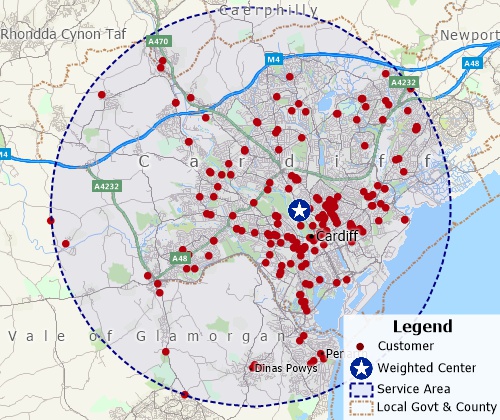
Weighted-center mapping tools can determine trade areas and identify valuable sites
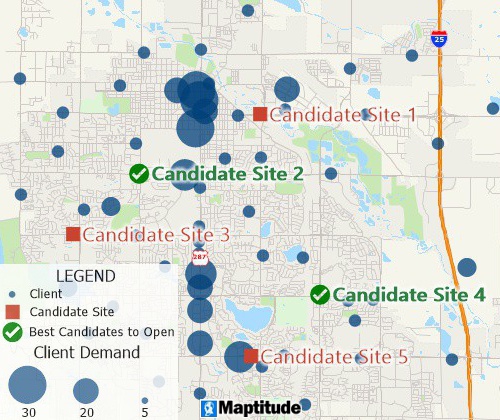
Facility location mapping tools can find suitable locations for expanding your business
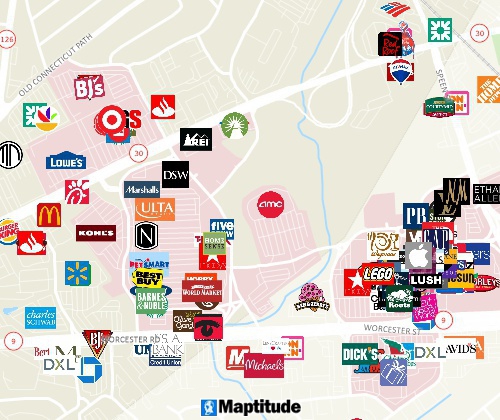
Mapping tool for locating businesses and competitors
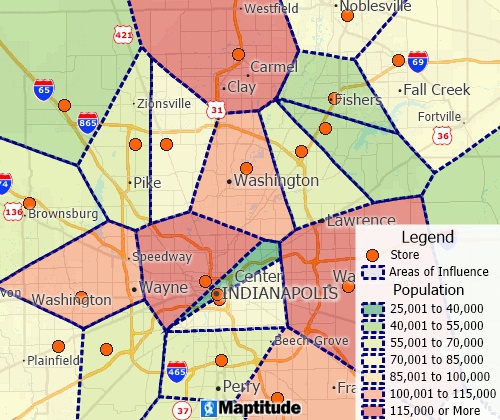
Thiessen polygon/Voronoi diagram map tools can create straight-line distance territories
Maps communicate information that is related to space and location in a remarkably efficient way, reducing volumes of information to a single, clear visual presentation. A weather map lets you know in an instant whether it will be cloudy or sunny, how warm or cold it will be, and whether it will rain or snow. Traffic maps let you know in seconds what route you should take to avoid an accident or steer clear of construction. In politics, history, advertising, and recreation, maps are a part of our everyday lives because they tell us so much of what we want to know.
To share your own information through the powerful medium of maps, there are several factors that should be considered. These include which custom map tools you require and whether you need high-quality map data. There are many mapping applications and Geographic Information Systems (GIS Software) on the market that you can choose between, ranging from:
The more expensive applications typically have professional, but often esoteric, cartographic map production tools. The free applications typically come with zero or limited data, low-quality data, or limited functionality.
The mapping software market is highly competitive but only Maptitude provides:
Maptitude (Maptitude mapping software) has flexible tools for map creation, customization, and map edits, and also supports more sophisticated tools such as enforced topology and adjacent area map coloring.
Maptitude provides the tools, maps, and demographic data that you need, with commands and special functions that let you tie in the data you use every day in your work. The MapWizard® automatic mapping tools create brilliant and informative maps with a single mouse click. Even more importantly, Maptitude provides ways for you to use the maps you create to analyze and understand how geography affects you and your organization or business.
Maptitude provides easy-to-use, professional mapping tools along with detailed USA data and at an affordable price. International versions of Maptitude mapping software are also available and come with demographic databases and geographic boundaries and features for each country.
Maptitude is designed to store, retrieve, manage, display, and analyze all types of geographic and spatial data.
Maptitude lets you produce maps and other graphic displays of geographic information for analysis and presentation. With these capabilities, Maptitude is a valuable tool to visualize spatial data. Maptitude is one of the most popular GIS software packages and has extensive functionality. The Maptitude capabilities include map and layer controls, visualization tools, geocoding, GIS mapping tools and geographic analytics (territory building tools, buffers, Thiessen Polygons, geographic overlay, hot spots, weighted center, shortest paths, drive-time bands, drive-time territories, measuring tools, desire lines, two-dimensional and 3D surface analysis, data classification, GPS support, internet mapping, and facility location), imagery/raster tools, map editing, drawing, digitizing, and relational database capabilities.
Mapping tools can be considered separately from mapping software or map applications. These are the actual functions that a geographic information system (GIS) provides. These tools allow the user to work with maps and geospatial data. In the table below we list the 27 most common mapping tools.
| Tool | Description |
| Add Data | Adds data to a map, including vector data, raster data, and tabular data. |
| Buffer | Creates a polygon at a set distance surrounding a feature. |
| Census and Demographic Data | Provides access to census and demographic data for a variety of geographic areas. |
| Clip | Extracts a portion of a feature based on a specified boundary. |
| Data Visualization | Provides a variety of tools for visualizing data, such as charts, graphs, and heat maps. |
| Dissolve | Merges overlapping features into a single feature. |
| Extract by Attributes | Selects features based on their attribute values. |
| Fleet Optimization | Optimizes the routing of multiple vehicles to multiple destinations. |
| Intersect | Finds the features that overlap a specified area. |
| Join | Combines two or more feature layers based on a common attribute field. |
| Label | Places text on a map to identify features. |
| Map Customization | Provides a variety of options for customizing maps, such as adding legends, titles, and north arrows. |
| Map Scripting | Automates GIS tasks using a scripting language. |
| Map Sharing | Publishes maps to the web or exports them to a variety of formats. |
| Merge | Combines two or more features into a single feature. |
| Overlay | Displays two or more feature layers on top of each other. |
| Polygon to Raster | Converts a polygon feature layer to a raster image. |
| Project | Converts data from one coordinate system to another. |
| Radius | Searches for features within a specified distance of a point. |
| Raster to Polygon | Converts a raster image to a polygon feature layer. |
| Reclassify | Changes the values of raster cells based on a specified classification scheme. |
| Redistricting/Territory Optimization | Creates boundaries, often commercial or political, that are optimized for certain criteria. |
| Report Generation | Generates reports that summarize and analyze data. |
| Route Planning | Creates routes between points, taking into account factors such as distance, travel time, and traffic conditions. |
| Site Selection | Identifies potential sites based on specified criteria. |
| Thematic Mapping | Creates thematic maps to visualize the distribution of data. |
| Zonal Statistics | Calculates statistics for raster cells within a specified zone. |
|
Maptitude Reviews and Testimonials |
|

Home | Products | Contact | Secure Store